 |
flinkLinux
flink Linux Kernel Modules
|
 |
flinkLinux
flink Linux Kernel Modules
|
All the basic functionality can be found in the file flink_core.c together with all necessary types and prototypes in flink.h. Bus Communication Modules implement this basic functionality for a given hardware interface.
The information for a specific flink device will be stored in a structure flink_device.
// ############ flink device ############
struct flink_device {
struct list_head list;
u8 id;
u8 nof_subdevices;
struct list_head subdevices;
struct flink_bus_ops* bus_ops;
struct module* appropriated_module;
void* bus_data;
struct cdev* char_device;
struct device* sysfs_device;
};
All flink devices which are present in a system will be inserted in a linked list.
A flink device will contain one or several subdevices. Those subdevices are represented by the structure flink_subdevice.
// ############ flink subdevice ############
struct flink_subdevice {
struct list_head list;
struct flink_device* parent;
u8 id;
u16 type_id;
u8 sub_type_id;
u8 if_version;
u32 base_addr;
u32 mem_size;
u32 nof_channels;
};
The following picture shows an example of a system with two flink devices, each containing two subdevices.
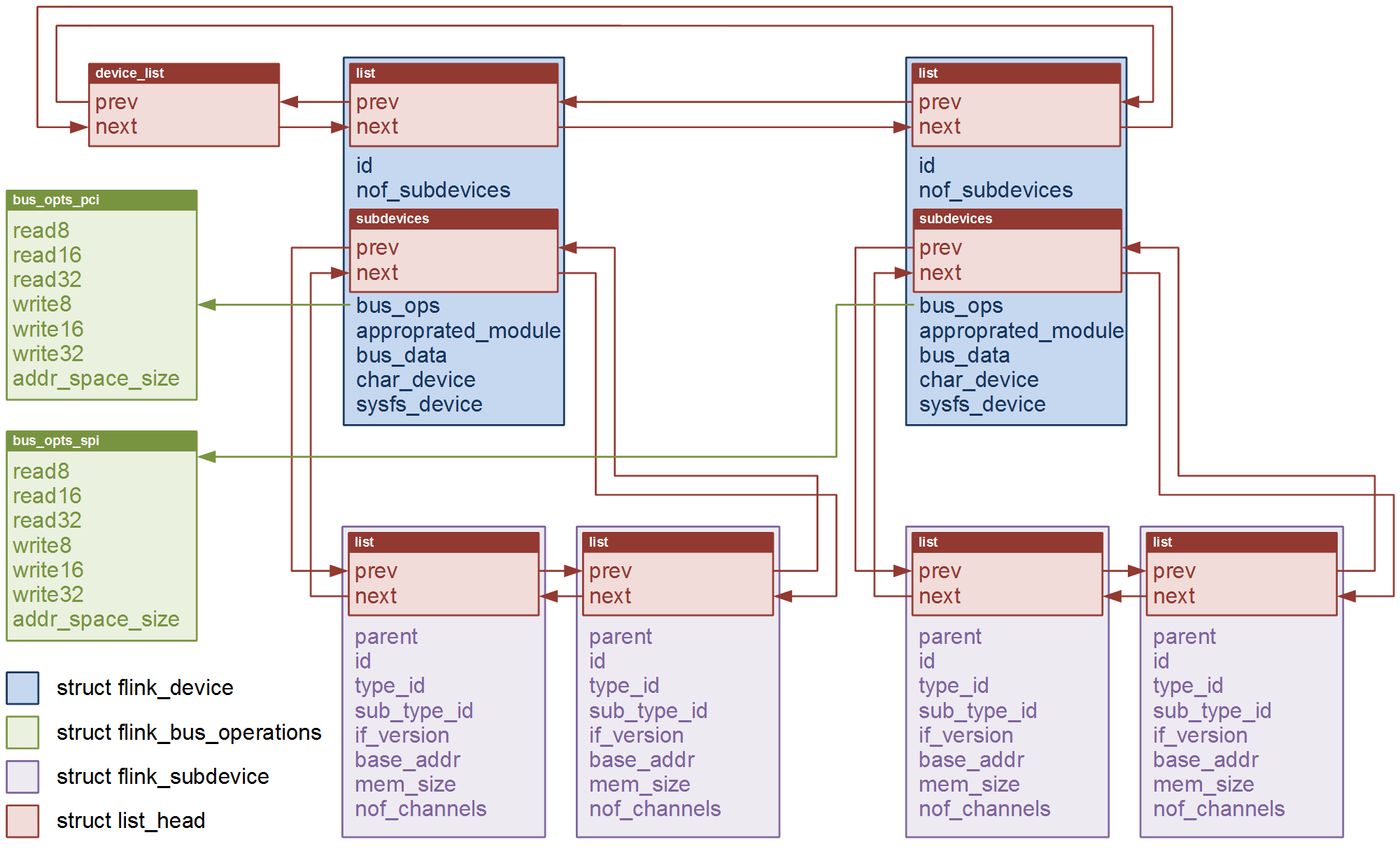
Obviously, a flink device must communicate with a given set of operations over its interface. However, we do not want to introduce any hardware dependency into flink_core.c. For this purpose we define a structure flink_bus_ops.
// ############ flink bus operations ############
struct flink_bus_ops {
u8 (*read8)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr);
u16 (*read16)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr);
u32 (*read32)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr);
int (*write8)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr, u8 val);
int (*write16)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr, u16 val);
int (*write32)(struct flink_device*, u32 addr, u32 val);
u32 (*address_space_size)(struct flink_device*);
};
This bus operations will later point to interface dependent functions. There is one more important data structure:
// ############ flink private data ############
struct flink_private_data {
struct flink_device* fdev;
struct flink_subdevice* current_subdevice;
};
An oben file is represented in Linux by the file structure. A parameter of type file is passed when calling read or write operations. file contains a field private_data which is used here to point to flink_private_data and holds the information about which device and subdevice will be targeted.
A flink device implements the following file operations
Several functions to manage devices and subdevices are exported for use in other kernel modules. The API can be found in API